Power supply repair and industry Power supply Repair
Power supply repairs are particularly in demand when electronic devices suddenly fail or no longer start after a voltage drop. The power supply unit converts the 230 volt mains voltage into a DC or AC voltage suitable for the respective device. Different types of power supply are used depending on the application. From linear power supply units to modern switching power supply units.
Typical causes of failure are defective components, unstable voltages, overheating or wear and tear due to ageing. In such cases, Mosertronik offers professional power supply repairs. We work regardless of the manufacturer, power class or device type.
Our repair service includes, among other things
- Replacement of defective components such as MOSFETs, IGBTs or diodes
- Replacement of aged capacitors and other components
- Testing of protective functions, control and thermal behaviour
- Load tests to ensure function during operation
Repairs are usually also possible for power supplies that are no longer available or have been discontinued. Thanks to extensive experience and targeted component sourcing, Mosertronik offers a reliable and sustainable solution. In the following article, we show the difference between classic transformers and modern switching power supplies and explain when which power supply should be used.
Types of power supplies
There are a variety of different power supply topologies that are used depending on the application and requirements. However, there are basically two main types of power supply: Transformers and switching power supplies. Both variants have their specific advantages and disadvantages and are used in different devices and environments.
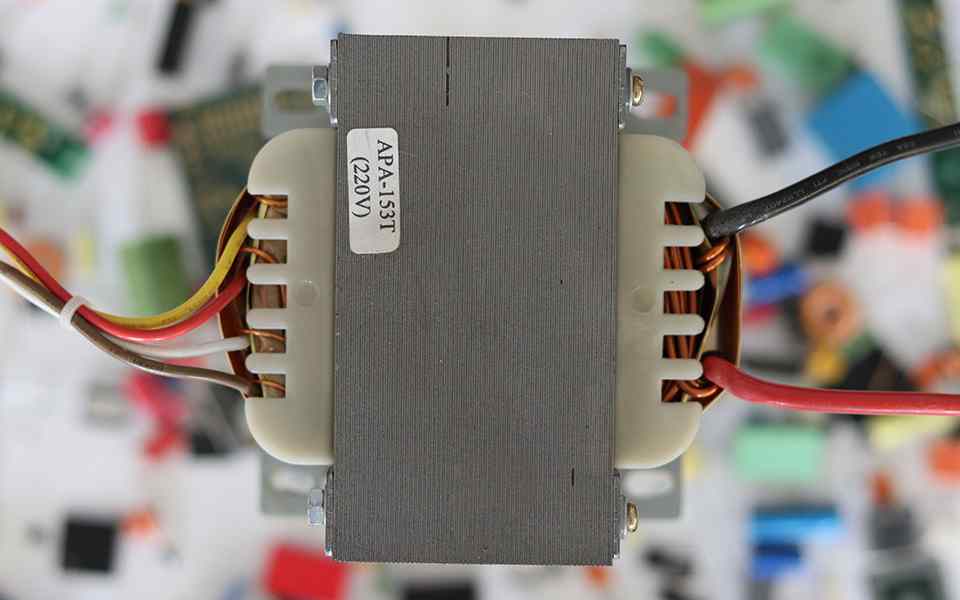
Transformers as power supply units
Transformers work exclusively with alternating current and are used to convert voltage by means of magnetic induction. They are available in numerous designs for different voltage ratios. Transformers were also used in power supply units for a long time, but have now been replaced in many areas by more efficient switching power supplies. The output voltage of a transformer is always AC voltage, which can then be converted into DC voltage using a rectifier.
Advantages transformer
- Very simple design
- Few components required
- Low electromagnetic radiation
Disadvantages transformer
- from a few 100W very large, heavy and expensive
- Output voltage difficult to adjust
- Poor efficiency
Switch-mode power supplies (SMPS) as power supply
A transformer is also used in a switched-mode power supply, albeit in a much more compact design and with a special layout. The main difference lies in the high switching frequency, which is significantly higher than the mains frequency. While classic transformers operate at 50 or 60 hertz, the operating frequency of switching power supplies is typically in the kilohertz range, usually between 20 and several 100 kHz.
This higher frequency means that the transformer can be much smaller, resulting in a more compact and lighter design. Depending on the circuit, switched-mode power supplies can be operated with both AC and DC voltage.
Advantages of SMPS
- Small and light even at high power
- Output voltage easily adjustable
- Good efficiency
Disadvantages of SMPS
- More components required
- Expensive to develop
- Higher electromagnetic radiation
Challenges with switching power supply repairs
The repair of switching power supply units requires special expertise, as these assemblies are much more complex than classic transformer solutions. The high switching frequency places special demands on measurement technology, component selection and soldering technology. Faults are often not immediately visible and require in-depth analyses. In addition, many switching power supplies are sensitive to component tolerances and incorrect spare parts, which makes repairs difficult without in-depth expertise. The thermal load and ageing of components such as IGBTs, MOSFETs or optocouplers must also always be taken into account when troubleshooting.

Defects and power supply repairs
The demands placed on power supply units are very high, especially in industry. Exact output voltages under load, minimal ripple and a long service life are required. For this reason, we not only offer a simple Power supply repairbut a complete overhaul. This involves replacing all components that have been subjected to particularly heavy use over many years. We only use high-quality components to restore the manufacturer's original specifications.
Test, inspections, measurements, test report
To ensure full functionality, every repaired power supply unit is thoroughly tested. This includes a function check, load test and a check of the electrical parameters to ensure compliance with the tolerances. If required, the output voltages are customised to the respective application. Also as part of a Power supply repair each device is extensively tested to ensure maximum reliability.
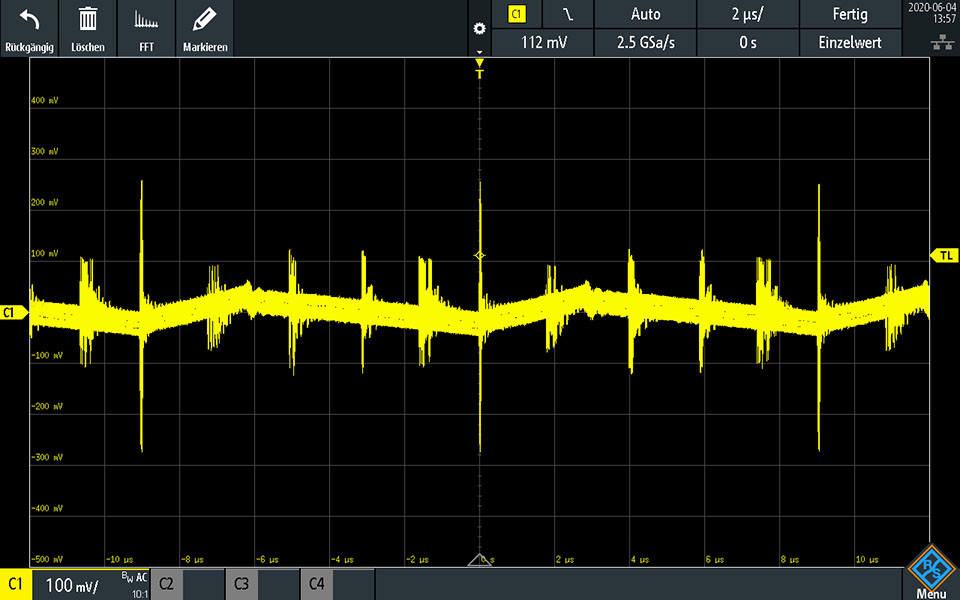
We can provide a detailed test report on request. This contains all relevant characteristic values such as apparent power, active power, output voltage, test current, efficiency, ripple and other measurement data. In the example shown, you can see a measurement of the Ripple voltage without DC voltage offset.